Coinbase Q1 financial report explained: Net profit plummeted 94% due to portfolio losses, and the company acquired Deribit to expand into derivatives
Compiled by: Felix, PANews
The U.S. cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase released its first quarter (Q1) financial report on May 8 local time. As market trading cooled compared to the rise after the U.S. election in the previous quarter, both revenue and net profit fell short of expectations.
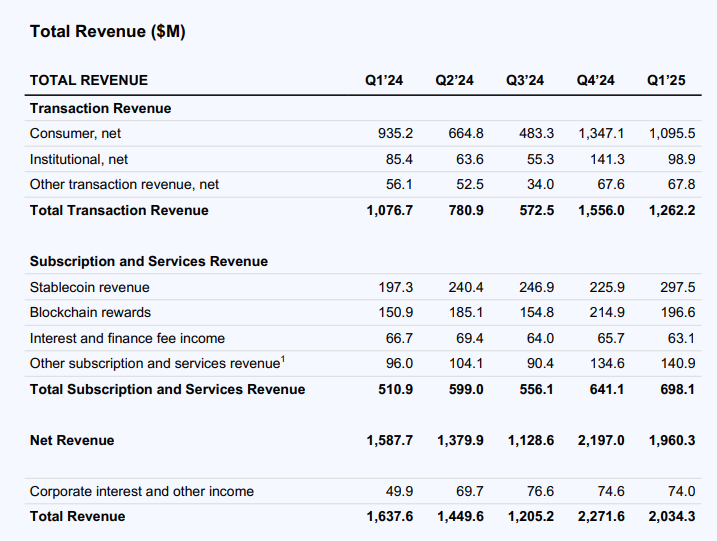
Adjusted net income was $527 million as of March 31. Earnings per share were $0.24, below the consensus estimate of $1.93. Total revenue was $2 billion, slightly below the expected $2.12 billion and below the $2.3 billion in the fourth quarter of 2024. Q1 trading revenue fell 19% to $1.2 billion, with trading volume falling 10%.
Perhaps affected by this news, Coinbase (COIN) shares fell 2.67% in after-hours trading, compared with a 5% increase in the previous trading day. COIN has fallen 16.83% since the beginning of this year.
income
The average volatility of cryptocurrency assets increased in Q1, with BTC hitting a record high in January. However, affected by tariff policies and macroeconomic uncertainty, cryptocurrency prices fell in tandem with the overall market decline. Compared with the end of the fourth quarter, the total market value of cryptocurrencies at the end of the first quarter fell 19% to $2.7 trillion.
Against this backdrop, Coinbase's revenue reached $2 billion, down 10% from the previous month; net income plummeted 94% from the previous month to $66 million, mainly due to a $597 million pre-tax loss on its crypto asset portfolio, most of which was unrealized losses. Adjusted net profit was $527 million, and adjusted EBITDA was $930 million.
Trading income
Coinbase's financial report shows that trading is its main source of income, accounting for more than 60% of its total revenue. Q1 trading revenue was $1.3 billion, down 19% from the previous quarter. Coinbase's total spot trading volume fell 10% from the previous quarter to $393.1 billion, but it was better than the global spot market, where trading volume fell 13% from the previous quarter. In terms of derivatives, Coinbase's trading volume reached $803.6 billion, and its market share continued to grow.
Among them, Q1 retail trading volume was $78.1 billion, down 17% from the previous month. Retail trading revenue was $1.1 billion, down 19% from the previous month, which was basically the same as the decline in trading volume. In terms of institutional trading, institutional trading volume was $315 billion, down 9% from the previous month, and institutional trading revenue was $99 million, down 30% from the previous month.
In addition to the impact of the macro background, the second factor for the month-on-month decline in revenue is the derivatives business. The financial report stated that Coinbase is investing in trading rebates and incentives to build liquidity and attract customers. These rebates and rewards have been deducted from institutional trading revenue.
Other trading income
Q1 Other Transaction Revenue was $68 million, flat sequentially. Base’s transaction volume increased 16% sequentially, but average revenue per transaction decreased 21%.
Subscription and services revenue
Subscription and service revenue was $698 million in Q1, up 9% from the previous quarter, mainly due to growth in stablecoin and Coinbase One revenue, with USDC hitting a record high of more than $60 billion in market value. However, blockchain reward revenue fell 9% from the previous quarter, partially offsetting this growth. The main reason for the decline was the decline in average asset prices from the previous quarter, especially ETH and SOL.
Stablecoin revenue grew 32% quarter-over-quarter to $298 million in the first quarter. Coinbase said the growth was partially offset by lower average interest rates. The average USDC holdings in Coinbase products grew 49% quarter-over-quarter to $12.3 billion.
Other subscription and services revenue was $141 million, up 5% sequentially. Coinbase One subscribers hit a record high in Q1, and Coinbase One Premium ($300 per month) also grew.
expenditure
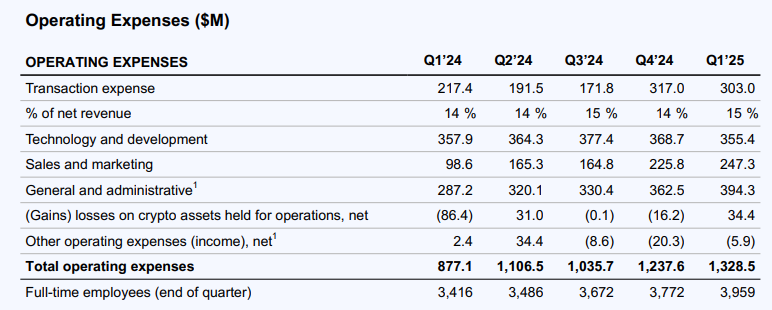
Total operating expenses for the first quarter were $1.3 billion, up 7% quarter-over-quarter, or $91 million, primarily due to increased variable expenses caused by market activity at the beginning of the quarter and losses on crypto assets held for operations. Technology and development, general and administrative management, and sales and marketing expenses increased by a total of $40 million, up 4% quarter-over-quarter, primarily due to increased marketing expenses (including performance marketing and USDC rewards) and increased customer support costs. At the end of the quarter, Coinbase's full-time employees increased 5% quarter-over-quarter to 3,959.
Transaction fees were $303 million, or 15% of net revenues, and decreased 4% sequentially. The sequential decrease was primarily due to lower client trading activity and lower blockchain reward fees associated with lower average asset prices.
Technology and development expenses were $355 million, down 4% sequentially. The decrease was primarily due to a decrease in personnel-related expenses despite an increase in headcount. General and administrative expenses were $394 million, up 9% sequentially. The increase was primarily due to an increase in customer support and personnel-related costs. Sales and marketing expenses were $247 million, up 10% sequentially.
Outlook
In April, Coinbase's total transaction revenue was approximately $240 million. Coinbase expects Q2 subscription and service revenue to be between $600 million and $680 million, as the expected month-on-month growth in stablecoin revenue will be offset by a decline in blockchain reward revenue due to falling asset prices; transaction fees will account for about 15% of net revenue; technology and development and general and administrative expenses will be between $700 million and $750 million.
It is worth mentioning that Coinbase has made efforts in the derivatives market. It announced that it would acquire Deribit, the world's largest Bitcoin and Ethereum options exchange, for US$2.9 billion, including US$700 million in cash and 11 million shares of Coinbase common stock, but the acquisition price is subject to customary adjustments. The transaction is subject to regulatory approval and other customary closing conditions and is expected to be completed by the end of the year. Last year, Deribit's open interest exceeded US$30 billion and its trading volume exceeded US$1 trillion.
“We expect Derebit to immediately improve our profitability and increase the diversity and durability of our trading revenue,” Coinbase Chief Financial Officer Alesia Haas said on the earnings call.
In addition, Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong said in an investor conference call that this quarter, Coinbase will launch a pilot project that allows businesses to use stablecoins for payments and spending.
Related reading: Record-breaking $2.9 billion merger: Coinbase swallows up Deribit, the king of options, and the crypto derivatives market is undergoing a huge change
You May Also Like

The Role of Blockchain in Building Safer Web3 Gaming Ecosystems
- Immutable Ownership of Assets Blockchain records can be manipulated by anyone. If a player owns a sword, skin, or plot of land as an NFT, it is verifiably in their ownership, and it cannot be altered or deleted by the developer or even hacked. This has created a proven track record of ownership, providing control back to the players, unlike any centralised gaming platform where assets can be revoked.
- Decentralized Infrastructure Blockchain networks also have a distributed architecture where game data is stored in a worldwide network of nodes, making them much less susceptible to centralised points of failure and attacks. This decentralised approach makes it exponentially more difficult to hijack systems or even shut off the game’s economy.
- Secure Transactions with Cryptography Whether a player buys an NFT or trades their in-game tokens for other items or tokens, the transactions are enforced by cryptographic algorithms, ensuring secure, verifiable, and irreversible transactions and eliminating the risks of double-spending or fraudulent trades.
- Smart Contract Automation Smart contracts automate the enforcement of game rules and players’ economic exchanges for the developer, eliminating the need for intermediaries or middlemen, and trust for the developer. For example, if a player completes a quest that promises a reward, the smart contract will execute and distribute what was promised.
- Anti-Cheating and Fair Gameplay The naturally transparent nature of blockchain makes it extremely simple for anyone to examine a specific instance of gameplay and verify the economic outcomes from that play. Furthermore, multi-player games that enforce smart contracts on things like loot sharing or win sharing can automate and measure trustlessness and avoid cheating, manipulations, and fraud by developers.
- Cross-Platform Security Many Web3 games feature asset interoperability across platforms. This interoperability is made viable by blockchain, which guarantees ownership is maintained whenever assets transition from one game or marketplace to another, thereby offering protection to players who rely on transfers for security against fraud. Key Security Dangers in Web3 Gaming Although blockchain provides sound first principles of security, the Web3 gaming ecosystem is susceptible to threats. Some of the most serious threats include:

Vitalik Buterin Challenges Ethereum’s Layer 2 Paradigm
